Energy management The term “energy management” is used nowadays in daily life for a broad range of measures and activities from monitoring up to controlling, for example. In the 80s, quality management was the first basis for defining standards based on supplementary management methods. The first version of the energy management standard, the DIN …
Weiterlesen
Announcement of a new iVision® Audit version Process-oriented remote auditing By loading this video you agree to the privacy policy of YouTube.Read more Load video Always unlock YouTube Due to different points of view, the issue of auditing is becoming more and more important both for the audited parties and the initiators of the very …
Weiterlesen
Announcement of a new iVision® Audit version
Process-oriented remote auditing
If you consider that “solely” one of these points applies to your situation, the utilization of our solution can help you to a considerable extent yet. This is especially so as the new ISO 19011:2018 already makes reference to remote audits and states that they are supposed to be adequate and well-balanced taking into account risks and chances.
iVision® – a brand of PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH (LLC)
The iVision Audit is a remote audit solution which provides a new basis for the performance of audits. The auditor or the respective expert conducts the audit on their home computer. It needs to be agreed in advance whether a co-auditor will be used on-site or whether the audited company will deploy a coworker as a co-auditor.
The co-auditor will be wearing data glasses through which the auditor will be able to see and hear exactly what the co-auditor will be hearing and seeing on-site. As a supplement to that, the auditor can supply additional information or instructions to the co-auditor via augmented reality.
Audit evidence can then be documented by means of photos and / or videos in order for them to be recorded in the subsequent audit report. The auditor can either assess the entire situation and the proof right away or later while creating the report.
Of course, corresponding conceptions with regard to different roles and users will be on file when it comes down to several clients / auditors. Data will be transmitted and stored in an encrypted manner, which will also hold true up to supplements to automated report creation. As another optional functionality, the system can be evaluated based on the audit and the respective underlying standards.
For that, the coverage rate of the audit scope will be taken as a basis and assessed in an automated manner based on the evaluation. Clients of PeRoBa Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH (LLC) already know this system from our audit reports.
Example for the application of iVision®
I would like to express my gratitude to Mr. Pfeifle CEO and his coworkers from the CTP GmbH (LLC) company in whose rooms we could film the iVision® Audit application.
We support you
The team of the PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH is happy to stand by your side if you have more questions in this context of if you would like to get recommendations for action. If you have any inquiries or if you would like support, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with us at: https://www.peroba.org/contact/ over any questions or concerns.
Your PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung GmbH (Management Consultancy) GmbH (LLC) team
DIN EN ISO 19011:2018 Guidelines on auditing management systems – Process-oriented auditing The new ISO 19011:2018 standard was published in July 2018. The German version DIN EN ISO 19011:2018 appeared in October 2018. ISO 19011 provides instructions on managing and directing an audit program, on planning and performing a management system audit as well as …
Weiterlesen
DIN EN ISO 19011:2018
Guidelines on auditing management systems – Process-oriented auditing
The new ISO 19011:2018 standard was published in July 2018. The German version DIN EN ISO 19011:2018 appeared in October 2018.
ISO 19011 provides instructions on managing and directing an audit program, on planning and performing a management system audit as well as on the competence and assessment of an auditor / audit manager and an audit team.
The structure and new contents of DIN EN ISO 19011:2018
First, it should be noted that the standard doesn’t follow the so-called high level structure, meaning the structure with 10 chapters analogously to ISO 9001. The standard continues to have 8 chapters.
The chapters are still, as follows:
▪ Passage 1 Scope
▪ Passage 2 Normative references (none)
▪ Passage 3 Terms and definitions
▪ Passage 4 Principles of auditing
▪ Passage 5 Managing an audit program
▪ Passage 6 Conducting a management system audit
▪ Passage 7 Competence and evaluation of management systems auditors and of audit teams
▪ Annex A provides additional guidance for auditors on planning and conducting audits.
Auditing risks and chances
In the chapter on principles of auditing, this passage has been supplemented by a new demand for a “risk-based approach”, which stretches right through the entire guidelines.
The chapter on the “audit program“ was structured in a new way and supplementary instructions with regard to risks were included. The audit program is more strongly connected to the strategic focus of the company. Furthermore, the requirements from DIN EN ISO 9001 like, consideration of the context of the organization, of identified risks and chances and the objectives of the organization are expanded.
The audit program is supplemented by instructions on management, especially of existing risks and on the performance of audits with regard to digital media. PeRoBa® auditors have been using data glasses, so-called smart glasses for audits for quite some time. This is supposed to serve the reduction of audit expenditures during follow up audits or the involvement of specialists.
In passage 5, the Plan – Do – Check – Act cycle by Deming is presented. Likewise, the coordination of audit activities is dealt with.
In Annex A, there are supplementary explanations, like, for instance, on the following:
iVision® – Smart Solutions by PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung GmbH
The performance of audits in highly complex surroundings becomes more and more of a challenge. Especially during remote audits, the utilization of new technologies can be an option for reducing expenditures and achieving objectives in a more efficient manner.
With the aid of the iVision® Audit Solution, an innovative technology, it is possible for us to reduce efforts for remote audits drastically. A coworker of the company is provided with our iVision® software including data glasses.
For example, an auditor is able to see the same things the coworker sees on-site as well by means of this technology. During this, the auditor could also be based on the other side of the world. Communication occurs likewise through data glasses. The auditor can communicate with the coworker on-site and give them instructions. This coworker performs the audit personally “on-site” instead of the auditor. That approach can be especially very helpful for involving audit specialists whose expert competence is solely required for a limited period of time.
Furthermore, the auditor can provide the viewing field of the coworker with visual information, clues and supplements. Thus, for example, an area the auditor wants to check out more precisely can be marked.
Due to the integration into the IT system, an automatically generated audit report can be created out of this connection and the auditor can further edit and process this auditing report within a very short time.
Conclusion
Requirements on auditors are more specified. The issues of knowledge, competence and skills all around the specialist topic of “internal audits” including the planning and performance of audits and follow-up activities are emphasized. Moreover, qualities like process knowledge, handling new media safely, confidence when it comes down to methods and reliable applications of professional judgment are required.
Personal demeanor, radiance and charisma as well as their direct contact to experts, executives and top management are supplementary requirements for auditors so that they can act as ambassadors for the management system. Besides, they need persuasiveness and a wealth of ideas on further developing the management system.
We support you
The team of the PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH is happy to stand by your side if you have more questions in this context of if you would like to get recommendations for action. If you have any inquiries or if you would like support, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with us at: https://www.peroba.org/contact/
Your PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH Team
iVision® – Smart Solutions by PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung GmbH Performing audits in highly complex surroundings is becoming more and more of a challenge. Especially with respect to remote audits, the utilization of new technologies can be a path to reducing efforts and achieving one’s aims more efficiently. The auditors from PeRoBa have also been using data …
Weiterlesen
iVision® – Smart Solutions by PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung GmbH
Performing audits in highly complex surroundings is becoming more and more of a challenge. Especially with respect to remote audits, the utilization of new technologies can be a path to reducing efforts and achieving one’s aims more efficiently. The auditors from PeRoBa have also been using data glasses, so-called smart glasses for performing audits for quite some time.
iVision® – Remote audits or respectively audits 4.0
With the support of this new and innovative technology, it is possible for us to reduce efforts while conducting remote audits tremendously. An employee of the respective company is then provided with our iVision® software and data glasses.
For example, an auditor is able to see the same things the coworker sees on-site with the aid of this technology. The auditor can actually be located on the other side of the world as well. Communication occurs also through the data glasses. The auditor can communicate with the employee on-site and give them instructions. This coworker performs the audit personally “on-site” instead of the auditor.
Besides, it is possible for the auditor to display visual hints and info and supplementations to the employee. For example, an area the auditor wants to inspect more precisely can be highlighted this way.
Out of this connection, proper integration with our IT system can create an audit report which is generated in an automated manner and which the auditor can further process and complete within an extremely short time.
iVision® – a brand of PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH
This is the statement of Dr. Scherb, the managing shareholder of the PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH on the successful milestones reached during this year:
„Our team and I are especially glad that the German Patent and Trademark Office granted us the patent for the “device and procedure for visual technical support of manual order picking processes” this year. This functionality serves as the basis for our auditing module with data glasses. As of now, Vision® is also among the best IT solutions for small and medium-sized companies! iVision® was honored with the Best IT of 2018 Innovation Award.
These are the driving forces for us to further develop iVision® and to implement customer requirements in an efficient and pragmatic manner.“
We support you
The team of the PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH is happy to stand by your side if you have more questions in this context of if you would like to get recommendations for action. If you have any inquiries or if you would like support, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with us at: https://www.peroba.org/contact/
Your PeRoBa® Unternehmensberatung (Management Consultancy) GmbH Team
The purpose of the 7 quality tools Errors and data can be collected, reasons for errors can be determined and investigated and errors can be prevented and improvements can be made sure by the 7 quality tools. These so-called 7 quality tools were originally put together by Ishikawa for use in quality circles. The 7 …
Weiterlesen
Errors and data can be collected, reasons for errors can be determined and investigated and errors can be prevented and improvements can be made sure by the 7 quality tools. These so-called 7 quality tools were originally put together by Ishikawa for use in quality circles.
The 7 quality tools are simple and efficient tools which will lead to a high degree of efficacy if they are used precisely.
A short description of the 7 quality tools comes next.
The easiest variety of this consists of a piece of paper with handwritten records on the systematic detection and depiction of different main errors.

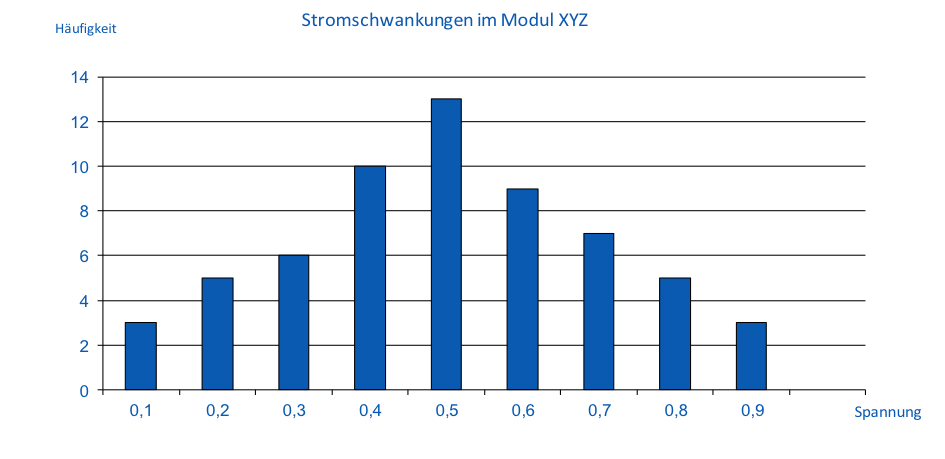
Data are put in order depending on the respective frequency of e.g., their occurrence over time. A histogram (a bar chart) is the graphical depiction of the frequency distribution of a quantity of data which were summarized. The depiction helps to classify individual results among a group of the same result or to determine the area where an individual result is expected. Mean values and distributions constitute important extensions of such histograms. The histogram is the basis of further methods like a superimposed bell-shaped curve; the normal distribution.
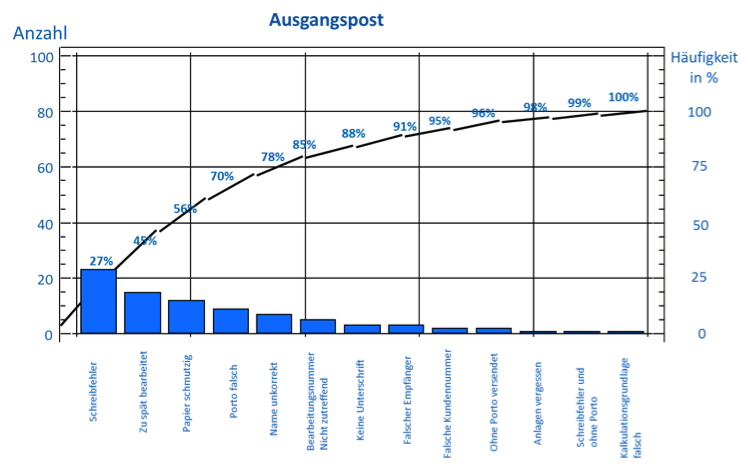
The Pareto depiction is another quality tool. It is a vertical bar chart for the graphical depiction of the reasons for problems. Influences can be arranged here depending on their significance. Important occurrences can be separated from irrelevant ones through the Pareto diagram. Other designations for this are 80-20 distribution or ABC analysis. This tool helps to detect the main reasons better and to process them efficiently.
Reasons for the development of problems can be classified and analyzed through a combination of the 5 Ms (machines, methods, materials, man, mission / Mother Nature) or the 7 Ms (machines, methods, materials, man, mission / Mother Nature, measurements, management). That will clarify if the problems respectively the errors might have several reasons which are frequently interconnected. 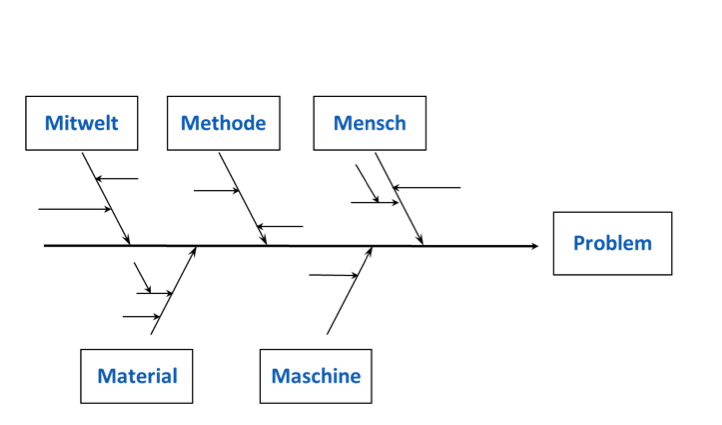
This is about separating and stratifying data from different sources. Different data are collected in order for them to be treated based on facts.
This is supposed to identify root causes so that improvement measures can be managed.
In many depictions, the method is referred to as brainstorming instead of stratification. Brainstorming is a basic entrance-level technique for looking for possible reasons for problems together in a group of people.
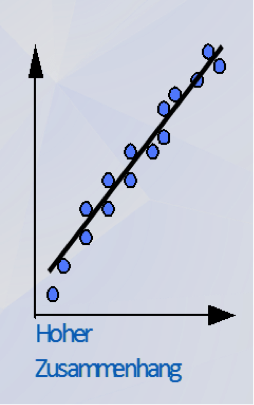
This is the graphical depiction of a correlation between two measured values. Correlations, connections, regularities and tendencies can be read off here.
This is an easy quality tool in order to check whether, e.g., a process operates within the tolerance limits and to make sure that it does. The results can be depicted graphically with the aid of the control chart. Furthermore, this tool is excellent for explaining and setting out the standard requirements from chapter 8.1 on “controlled conditions”. More information on that will be posted in one of the next publications.

[/et_pb_text][et_pb_code _builder_version=”4.2.2″ vertical_offset_tablet=”0″ horizontal_offset_tablet=”0″ z_index_tablet=”0″]
What are the 7 Quality Tools (Q7)?
The 7 Quality Tools (abbreviated as Q7, QM Tools) are a collection of proven methods for quality assurance. With them, users can document errors in a strongly targeted manner and collect data, which can be used for avoiding these very mistakes in the future. The methods had already been compiled by Japanese chemist Ishikawa Kaoru in 1943 but they have not lost any of their relevance up to now.
What methods do the 7 Quality Tools include?
The Q7 consist of error collection lists (also data collection sheet), histograms, Pareto charts, Ishikawa diagrams (cause-and-effect diagrams), stratification (colloquially referred to as brainstorming), correlation diagrams and control charts.
What are the M7 (7 Management Tools)?
In contrast to the analytical and quantitative methods of the Q7, the 7 Management Tools (M7) provide a collection of tools which make it possible to structure and analyze verbal information. To present it in a simplified manner, problem solving occurs here through a process of identifying the problem, finding the solution and implementing the solution.
What other QM Tools are there on top of the Q7?
Aside from the classic Q7, FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis), PPAP (Production Part Approval Process), QFD (Quality Function Deployment) as well as SPC (Statistical Process Control) are utilized most often in practice.